# AI assistant (preview feature)
Please note
The AI assistant is not currently intended for use in production environments.
The AI assistant lets you analyze and edit recognized document content or use it in ELO using artificial intelligence.
You can select predefined functions or enter your own questions and actions.
Information
This preview feature has to be enabled and configured by an administrator before it can be used. Separate documentation (opens new window) is available for administrators.
# Call
With the document open, select the AI assistant via the button with the sparkle icon or keyboard shortcut CTRL + spacebar.
# Interface
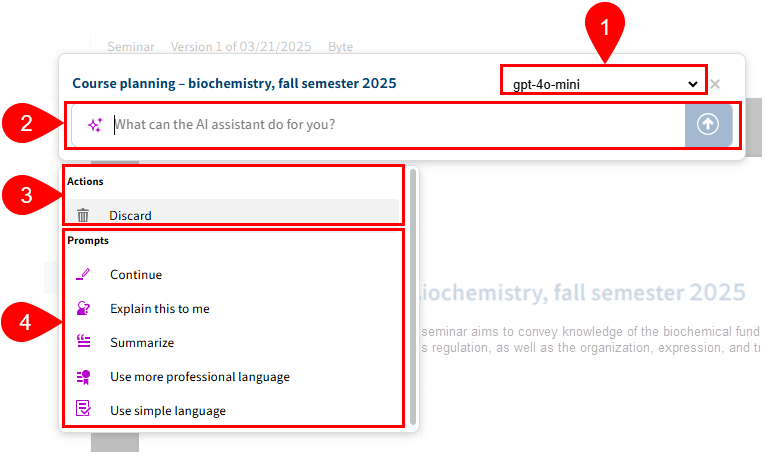
1 Language model: Select a language model. Your administrator can configure multiple language models. Once a prompt has been submitted, the model is set for the chat. Open the AI assistant again to switch the model via the drop-down menu. If only one model is configured, no drop-down menu or model name are shown.
2 Input field: Submit a custom prompt for the document. If you have submitted multiple prompts for the document, you can navigate through the message history using the arrow keys.
3 Actions: Only Discard is available when you open the AI assistant. More actions appear once you have started a chat.
4 Prompts: The prompts are sent to the configured language model. Five preconfigured prompts are available as standard. Administrators can add more prompts.
# Actions
The following actions are possible:
- Save data: This action is only offered during metadata extraction. It saves the values in the document's metadata.
- Start search: Triggers a search in the ELO repository using the response text. This action only makes sense with short responses. It can be used to search for customers in the repository, for example.
- Create feed post: This can be used to document who has done what for tracking purposes. The feed post is visible after the repository has been refreshed.
- Try again: If the answer is not satisfactory, you can send the prompt to the language model again with the same context.
- Discard: All actions and prompts are discarded. The AI assistant closes.
# Prompts
# Preconfigured prompts
- Use simple language: The content of the document is written in a clear, easy-to-understand, and accessible way. This is done by using short sentences and simple words, and avoiding technical terms or complex sentence structures.
- Explain this to me: This prompt generates a concise and structured explanation of the contents of the document.
- Use more professional language: A more formal, objective, precise writing style is used. A neutral tone is used, as is common in business and academic communication. This instruction helps tailor content for professional audiences, such as for reports, official documents, or presentations.
- Continue: Prompts the AI assistant to continue a text it has started. The language model uses the style, tone, and content of the existing text to generate a consistent and thematically appropriate continuation.
- Summarize: Instructs the system to reduce the document to its key content. Main points, arguments, and events are presented in a condensed form.
Please note
If the AI assistant is unable to return document-specific responses, this may be because it is unable to access the document's full text. Go to Metadata > Options and check whether Add to full text is enabled.
# Prompts created by administrators
Administrators can add more prompts (called custom prompts). You will recognize this type of prompt by the sparkle icon.
Example: List course participants
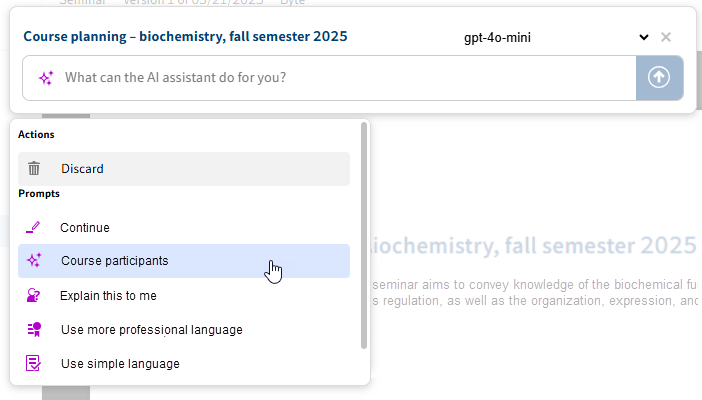
In our scenario, we are working in student administration and want to identify and list the participants in a course planning document. The custom prompt Course participants has been created with the following user prompt:
Which students are enrolled in this course? List them in a table.
Open the document you want to analyze. In our example, we select a course planning document that contains course participants.
Select the prompt (here: Course participants) in the AI assistant.
The AI assistant provides a response in the format requested.
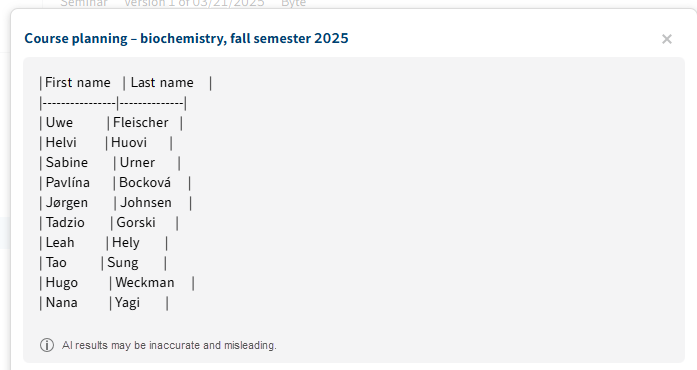
# Extract text from document
It is possible to extract specific text passages from a document and have them analyzed by the language model.
This function is recommended in two cases:
- The provided language model can only process a limited amount of context.
- Your document is very extensive and you only want to chat about a specific section (example: multi-page contract where only a specific clause is relevant to you).
Method
- On the ribbon, select View > Image preview.
- Hold down the CTRL key. Left-click and box in the section of the document you want to analyze.
- Release.
The extracted text appears in the AI assistant.
You can now chat with the language model about this text.
Information
Full text is not available when using this function.
# Metadata extraction
The AI assistant can help you enter metadata. Metadata can be extracted from the document and stored in the corresponding fields of a target metadata form in ELO. Metadata extraction only works with gen. 2 metadata forms.
Metadata extraction must have been configured by the administrator.
You will recognize this prompt type by the combined sparkle icon with a table in the background.
Example: Course data extraction
In the following example, the AI assistant will extract course data from a course planning document. Data should be assigned to fields of different aspects. Configuring this is described in the administrator documentation (opens new window).
Open the document you want to extract data from. In our example, we select a course planning document that contains course participants.
Select the metadata extraction prompt (here: Course data extraction).
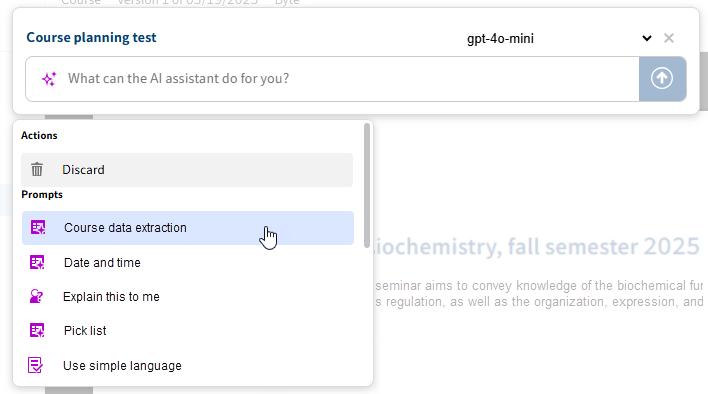
The AI assistant shows a table with all configured aspects and assigns the values to the corresponding field names.
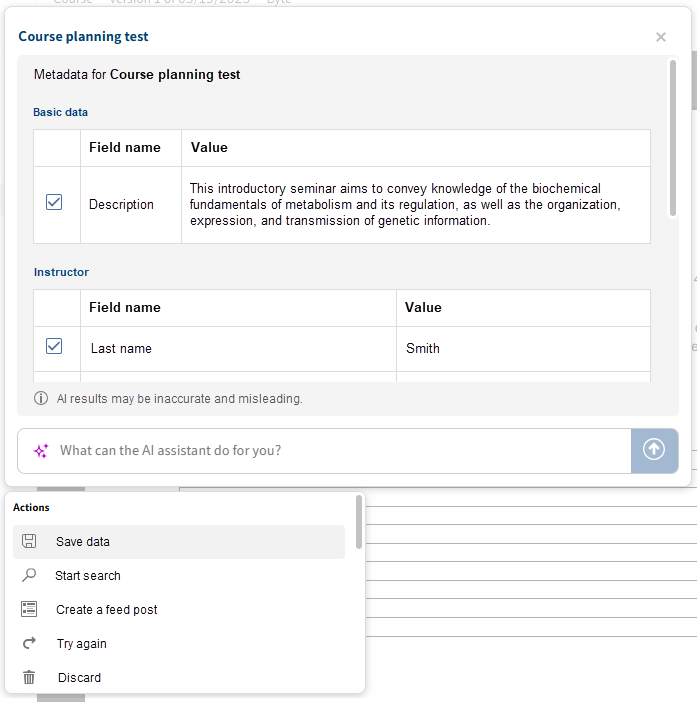
Check whether the values have been assigned correctly. If you do not want to keep certain values, uncheck the corresponding box.
Select the Save data action.
The values are saved in the document's metadata.
After saving, it is possible to create a feed post. The aspects and field names are listed with the extracted values in the feed post.
Information
Refresh ELO to display the stored metadata and feed posts.