# Metadata
This chapter describes how the synchronization of metadata from or to SharePoint Online works and can be configured.
# What is metadata?
In SharePoint Online, metadata refers to the non-system-relevant columns in document libraries. You can find more information on SharePoint Online, for example, on creating document libraries or user-defined columns, in the SharePoint documentation (opens new window).
In ELO, metadata is the fields of index and aspect forms. You will find more information on ELO index forms (opens new window) and aspect forms (opens new window) in the documentation.
# Supported columns
In SharePoint Online, only specific columns can be transferred to ELO.
User-defined columns are supported if they are one of the following types:
- Text
- Date and time
- Multi-line text
- Number
- Yes/No
- Hyperlink
- Currency
Of the system columns that SharePoint provides, the following columns are supported:
| Name | Metadata rule |
|---|---|
| Compliance object ID | *\*\ComplianceAssetId |
| Title | *\*\Title |
| Created | *\*\Created |
| Changed | *\*\Modified |
| Check-in comment | *\*\_CheckinComment |
| Item child count | *\*\ItemChildCount |
| Folder child count | *\*\FolderChildCount |
| Name setting | *\*\_ComplianceFlags |
| Storage name | *\*\_ComplianceTag |
| Storage name used. | *\*\_ComplianceTagWrittenTime |
| Name used by | *\*\_ComplianceTagUserId |
| Comment count | *\*\_CommentCount |
| Like count | *\*\_LikeCount |
| App created by | *\*\AppAuthor |
| App edited by | *\*\AppEditor |
These columns are read-only, i.e. you cannot transfer metadata from ELO to SharePoint.
# Metadata mapping
To link metadata fields between SharePoint Online and ELO, a field mapping must be defined. This can either be created for each synchronization job in the respective configuration, or globally in the settings, whereby the synchronization job configuration links have priority.
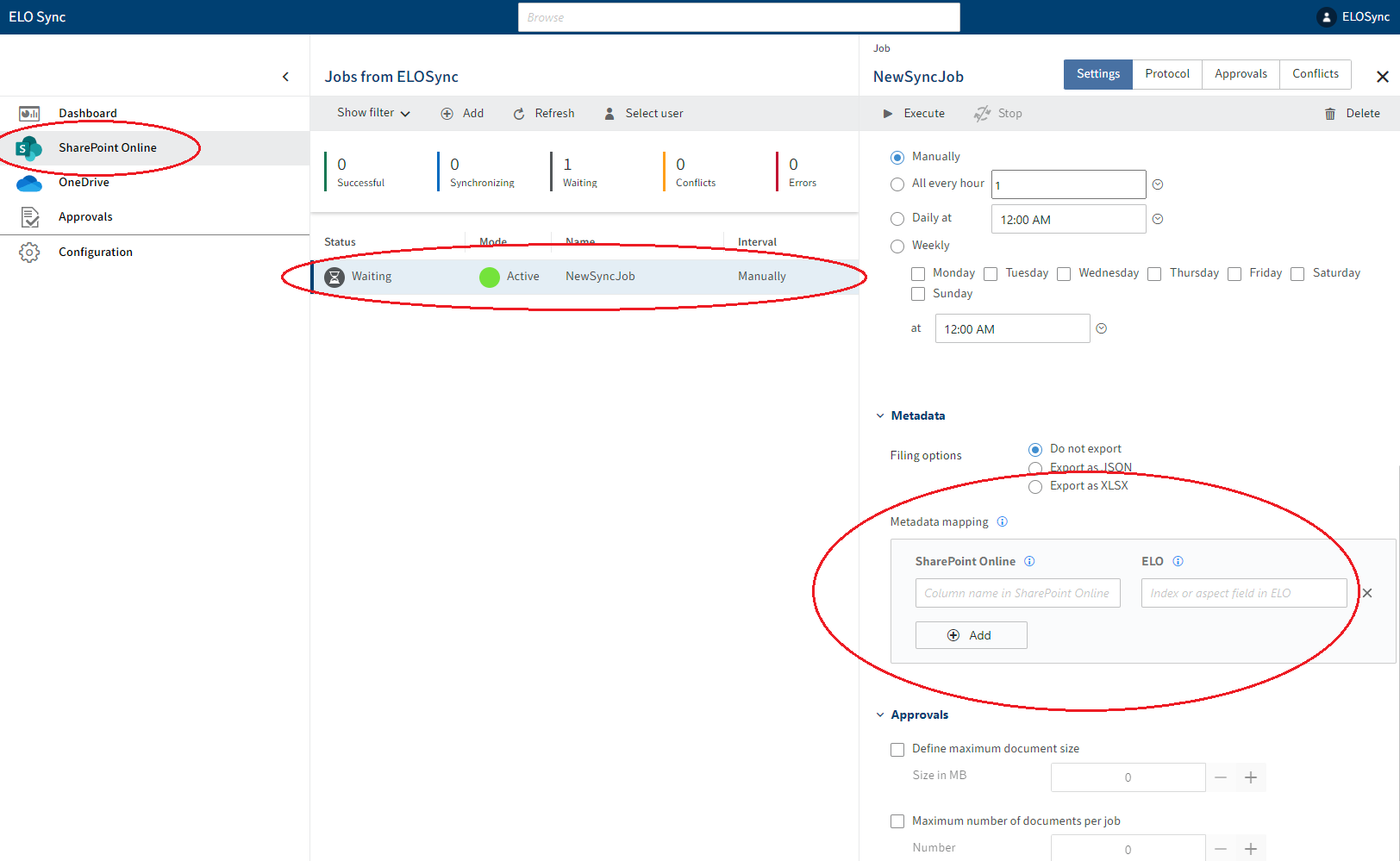
Metadata mappings in the synchronization job configuration
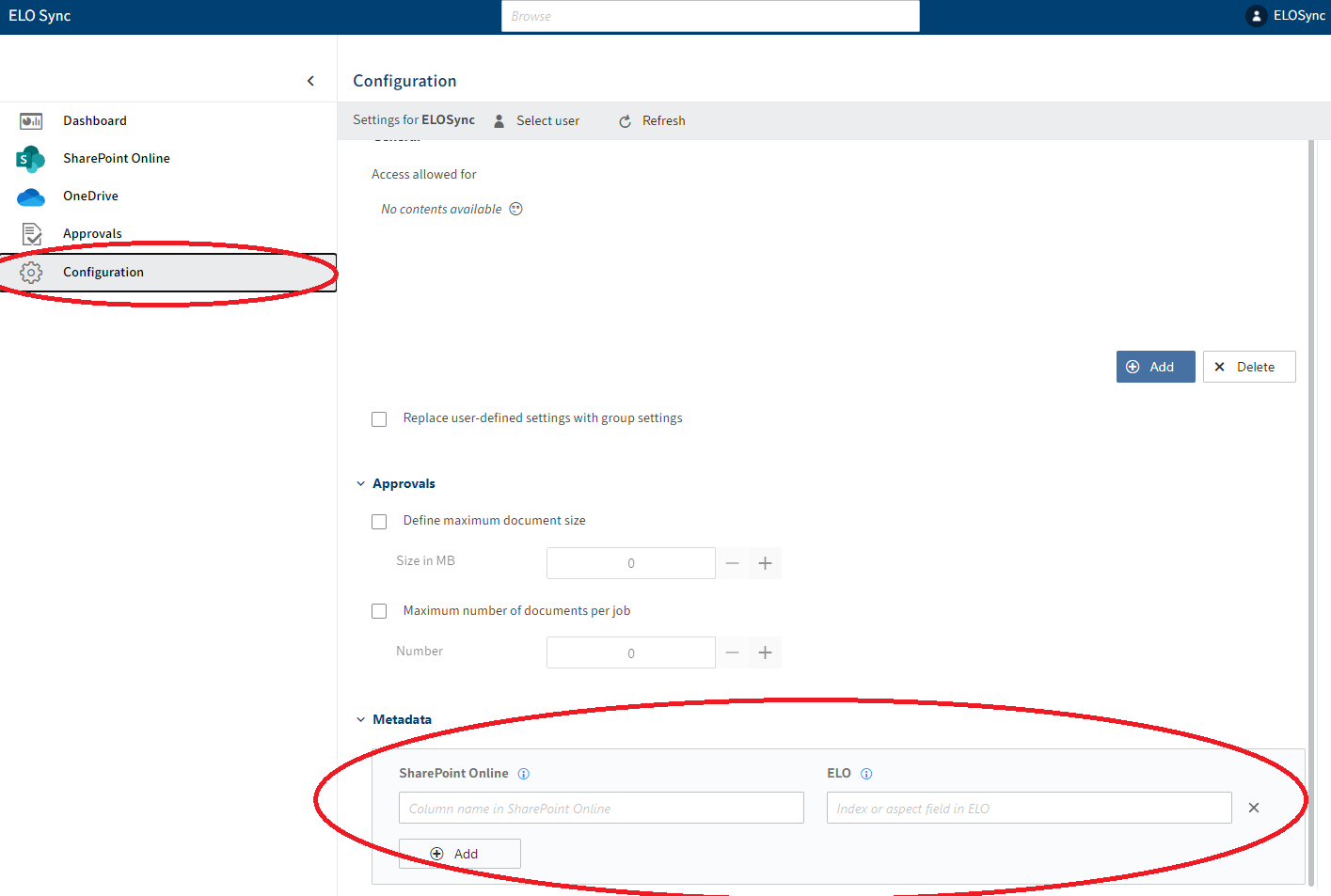
Metadata mappings in the global configuration
If a field could not be mapped, the metadata is not transferred for the field.
# Metadata mapping structure
Mappings can consist of several parts and are separated by a "".
# Mapping structure for SharePoint Online
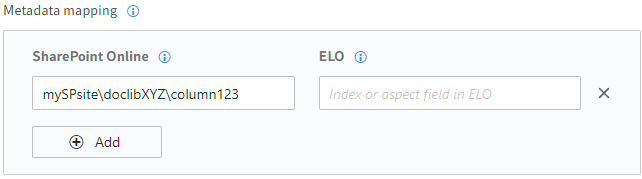
The structure of a SharePoint Online mapping may look as follows:
SiteName\ListName\ColumnName
Site and list names are optional here. To prevent confusion (e.g. a column from another list), mappings should contain as much information as possible.
Example:
# Mapping structure for ELO index and aspect fields
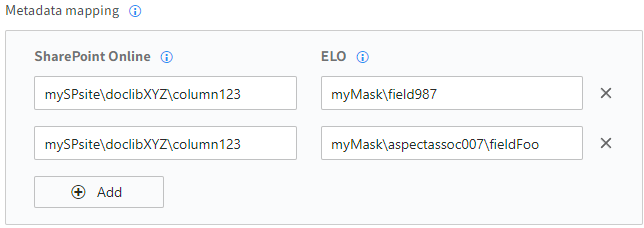
The structure of an ELO mapping may look as follows:
Index fields: MaskName\FieldName
Aspect forms: MaskName\AspectAssociation\FieldName
Form names and aspect mappings are optional here. To prevent confusion (e.g. a column from another list), mappings should contain as much information as possible.
Example:
# Wildcards
In addition, the two wildcards "*" and "?" can be used in the mappings. Here, "?" represents any character and "*" represents an unlimited number of any characters.
Example:
mySPsite\doclib*\column1?3 myMask\*\fieldF??
# Field mapping
Field mappings can be made both in the settings of the respective synchronization jobs and in the global settings. The mapping in the synchronization job settings has a higher priority here, i.e. if a field mapping was defined in the synchronization job settings and in the global settings, only the synchronization job settings are taken into account.
The respective mappings are resolved from the smallest unit to the largest, i.e. from back to front. Therefore, a mapping is first performed on the column or field name.
Based on the example from the section Mapping structure for SharePoint Online mySPSite\\doclibXYZ\\column123, the mapping is resolved in the following order:
- column123
- doclibXYZ
- mySPSite